Content
About the statistics
Definitions
-
Name and topic
-
Name: Deaths
Topic: Population
-
Next release
-
-
Responsible division
-
Division for Population Statistics
-
Definitions of the main concepts and variables
-
Mortality rates
The frequency of deaths in the population. In most cases the rate is multiplied by 1 000 so that it can be interpreted as the number of deaths per 1 000 persons.Infant mortality
Number of deaths per 1 000 live births among children under the age of one.Probability of death
Probability of death for a man/woman at age x is the probability that he/she will die before he/she reaches the age of x + 1. Probability of death is estimated for each age level separately for men and women and is used inter alia to estimate life expectancy. Probability of death is not the same as age-specific mortality rates.Life expectancy - remaining lifetime
Life expectancy or mean lifetime is the number of years a new-born can expect to live under current mortality conditions (period mortality). Life expectancy is estimated on the basis of the age-specific mortality probabilities in the period. Expectation of life is estimated for the various age levels.Calculation method - life expectancy and mortality tables
The mortality table is based on the probability of dying between two age levels (number of years). The probability is indicated with the symbol
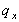
in which x stands for age x years.
The point of departure is a selected cohort of 100 000 persons of the same sex (l 0 =100 000), in which survivors at age x are
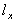
The number of persons who die are estimated for each age level.
The mathematical formula is as follows:
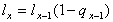
in which
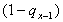
is the probability that a person aged x-1 will be alive one year later.
The number of deceased persons by their exact age x to x+1 year in the selected cohort are given as:
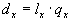
To calculate the expectation of life at age x we need the auxiliary aggregates contemporary survivors and total remaining lifetime.
The contemporary survivors of age x,
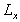
are the average number of persons of age x. If the deaths are assumed to fall evenly throughout the year, contemporary survivors are:
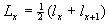
Total remaining lifetime at age x is the number of years
contemporary survivorxers in the cohort have to live: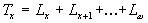
in which
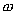
is equal to the highest age.
Expectation of life at age x is equal to the total of remaining years of life at age x, divided by the number of survivors at age x.
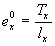
Age in the published tables is age in number of years at the time of death.
Residence
Sex
