Content
Published:
This is an archived release.
Grim prospects
Norwegian industrial managers report a decline in total output towards the end of 2008. Poorer demand was the main reason for this development. Indicators covering the short-term outlook imply a steep decline in the business cycle.
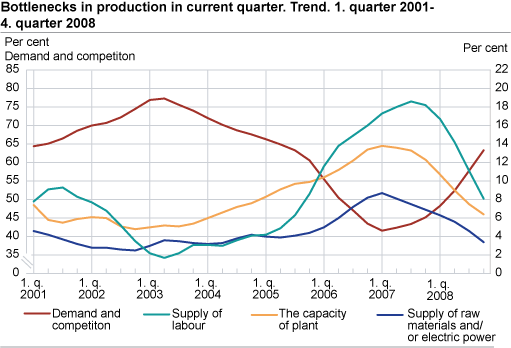
According to the business tendency survey, the Norwegian manufacturing industry experienced a decline in output and employment in the fourth quarter of 2008. Poor results for sectors producing intermediate goods were the reason for this development. Total stocks of orders fell due to a decline in new orders from domestic and export markets, while market prices continued to rise. Lack of demand is a growing concern among Norwegian industrial managers. High growth in stocks of finished goods supports this view. However, lack of capacity and shortage of qualified labour no longer seem to pose a major problem. The number of working months covered by the current stock of orders is somewhat lower than recorded in the third quarter, but the result is still quite high seen in a historical perspective. Average capacity utilisation is estimated to be 80.2 per cent. International comparisons of average capacity utilisation are available from EUROSTAT .
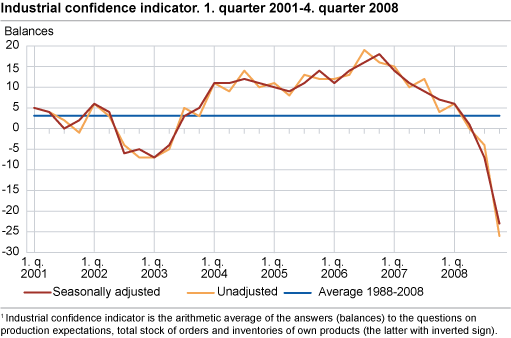
The general short-term outlook is considered to be negative. Expectations of a further decline in production, new orders and export market prices support this result. A growing number of industrial managers claim to be considering a reduction in planned gross capital investments. Prospects of poor demand and a shortage of venture capital are mentioned as reasons for such a decision. The industrial confidence indicator is estimated at -23 (seasonally-adjusted net figure) in the fourth quarter. This is far below the historic average and indicates a steep decline in the business cycle. International comparisons of the industrial confidence indicator are available from EUROSTAT (EU) and the Swedish National Institute of Economic Research (Sweden).
Poor results for sectors producing intermediate goods
Sectors producing intermediate goods (wood and wood products, pulp, paper and paper products, the chemical industry, basic metals and so on) experienced a further a decline in output and employment. A low level of new orders from both domestic and export markets was the reason for this development. The domestic market appears to be hugely affected by a harsh slowdown in the construction business, which is creating a poor market for building materials. With regard to the export markets, several sectors appear to have been hit by the fall in the global demand. Export prices are down in spite of the weaker Norwegian currency. Lack of demand is a growing concern among the respondents in question. However, lack of capacity and shortage of qualified labour no longer seem to pose a major problem. The number of working months covered by the current stock of orders is lower than recorded in the third quarter, and average capacity utilisation is estimated to be 77.9 per cent. The general short-term outlook is considered to be negative. Expectations of a further decline in production, new orders and market prices support this result. A huge majority of the industrial managers claim to be considering a reduction in planned gross capital investments.
Still high production of capital goods
Sectors producing capital goods (machinery and equipment, offshore-related activity and so on) experienced a very high level of production, but the growth rate was close to neutral. Total stocks of orders fell due to a decline in new orders from domestic and export markets. Many respondents also mentioned that there is a higher risk of cancellations of existing orders. Market prices continued to rise in the fourth quarter but the growth rate shows signs of levelling out. Lack of demand is a growing concern among the respondents in question, but fewer indicate lack of capacity or shortage of qualified labour. Average capacity utilisation is estimated to be 85.8 per cent in the fourth quarter. The number of working months covered by the current stock of orders is somewhat lower than recorded one year ago, but still remains at a very high level. The indicator covering the general short-term outlook is changing from neutral to negative, and a growing number of industrial managers claim to be considering a reduction in planned gross capital investments.
Rising prices on consumer goods
Sectors producing consumer goods (like the food industry, publishing, pharmaceutical industry and so on) report that the growth in total output was levelling out in the fourth quarter. Poorer demand from export markets seems to be the reason for this result. A decline in new orders for durable consumer goods like furniture partly explains this development. Total employment fell in the second half of 2008, and the decline grew stronger towards the end of the year. Market prices, however, continued to rise. A strong growth in prices of food products was the main reason for this. Average capacity utilisation is estimated at 77.7 per cent in the fourth quarter. The indicator covering the general short-term outlook is changing from positive to negative. Expectations of lower demand in export markets and a further decline in employment support this result.
| Industry | Prospects | Background | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Food products, beverages and tobacco | + | Growth in output and capacity utilisation. More or less unchanged level of employment. Increase in demand from the domestic market, while demand from the export market is more or less unchanged. Many managers report rise in market prices. The general outlook for Q1 2009 is judged as better. This view is supported by expectations of further rises in production, demand and market prices. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Wood and products of wood | -- | General decline in the construction industry is affecting the producers of wood and wood products. A large number of managers report lower levels of production, capacity utilisation and employment. Many managers are considering a reduction in planned gross capital investments. A large number of managers consider the general outlook for Q1 as worse, and a further decline in output, capacity utilisation, employment, new orders and market prices is expected in the forthcoming quarter. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Pulp, paper and paper products | - | Reduced output, capacity utilisation and employment. Decline in new orders, while export market prices have risen. The general outlook for Q1 is considered as negative. The level of production and export market prices are expected to rise, while total stock of orders and domestic market prices are expected to decline. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic chemicals | -- | Reduced levels of production, capacity utilisation and employment. Decline in new orders from the domestic and export market. Growth in market prices. Many managers indicate poor demand as a limiting factor for production. General outlook for Q1 is judged as worse, and managers are considering a reduction in planned gross capital investments. The levels of output, employment and new orders are expected to decline in the forthcoming quarter. Market prices are also expected to be reduced. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Basic metals, non-ferrous | -- | A large number of managers report that lack of demand limits production. In Q4 output is reduced together with capacity utilisation and employment. Lower levels of new orders and market prices. General outlook for Q1 is considered as worse by a large number of managers. Reduced levels of production, employment, new orders and market prices are expected in Q1. Reduction in planned gross capital investments. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Engineering, total | - | Overall, the engineering industries have reduced the level of new orders and decline in the total stock of orders. An increasing number of managers report poor demand as a limiting factor for production. Output and employment are more or less unchanged in Q4, while market prices are up. General outlook is judged as worse, and the levels of production and employment are expected to decline in Q1. A further decline in new orders is expected, while market prices are expected to remain more or less unchanged. Many managers are considering a reduction in planned gross capital investments. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Metal products | - | Average capacity utilisation has dropped and the level of production is reduced. Lower levels of employment and new orders. The average number of working months covered by the current stock of orders is reduced. Domestic market prices are more or less unchanged, while export prises are reduced. Many managers judge general outlook for Q1 as worse, and a further decline in output, employment and new orders is expected. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Machinery and equipment | -(+) | More or less unchanged levels of production and employment. Decline in new orders from the domestic and export market. Rise in market prices. Many managers report poor demand as a limiting factor for production. Reduction in planned gross capital investments, and general outlook for Q1 is considered negative. The levels of production and employment are expected to rise, while the level of new orders is expected to be further reduced. A further rise in market prices is expected. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Electrical and optical equipment | -(+) | Growth in output, capacity utilisation and employment. Reduced level of new orders from the domestic and export market. Rise in market prices. Poor demand is a limiting factor for production. General outlook for Q1 is judged as worse. This view is supported by expectations of lower levels of production, employment and new orders. Domestic market prices are expected to increase, while export prices are expected to remain more or less unchanged. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Offshore-related activity incl. transport industry | -(+) | Reduced levels of production, capacity utilisation and employment. Many managers report a lower level of new orders, especially from the export market. Lack of qualified labour is still a limiting factor for production, but fewer managers than in the previous survey support this view. General outlook for Q1 is considered worse, and a further decline in output and employment is expected. The level of new orders from the domestic market is expected to rise, while new orders from the export market are expected to remain more or less unchanged. Domestic market prices are expected to be more or less unchanged, while export prices are expected to drop. Reduction in planned gross capital investments. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| The column for Prospects shows an overall evaluation of the present situation and expected short-term developments using the symbols + and -. The following codes and constellations are used: |
++
+ ² - -- -(+) +/- |
Very good
Good Stable Poor Very poor Poor, but with certain positive indications A situation where the + and - factors even out. |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Important announcement: New classification being implemented shortlyAs from the first quarter of 2009, a new version of Eurostat’s industry classification, NACE, will be in use. The Business tendency survey (BTS) is affected by the change of nomenclature from the publication of the first quarter 2009 results. Click here to read more about the implications for users, calculation and dissemination. |
Additional information
The statistics provide current data on the business cycle for manufacturing, mining and quarrying by collecting business leaders’ assessments of the economic situation and the short term outlook.
Contact
-
Edvard Andreassen
E-mail: edvard.andreassen@ssb.no
tel.: (+47) 40 90 23 32
-
Ståle Mæland
E-mail: stale.maeland@ssb.no
tel.: (+47) 95 05 98 88