Content
Published:
This is an archived release.
Continued weak growth in Mainland GDP
According to seasonally-adjusted figures, gross domestic product for Mainland Norway rose by 0.2 per cent in the 2nd quarter of 2015, after three quarters of weak development. The weak trend is particularly seen in industries supplying the petroleum industry.
| 2014 | 3rd quarter 2014 | 4th quarter 2014 | 1st quarter 2015 | 2nd quarter 2015 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1Figures for the last two years are preliminary. | |||||
| Gross domestic product | 2.2 | 0.4 | 0.9 | 0.1 | -0.1 |
| Gross domestic product Mainland Norway | 2.2 | 0.0 | 0.4 | 0.3 | 0.2 |
| Petroleum activities and ocean transport | 2.1 | 1.7 | 2.5 | -0.8 | -1.0 |
| Final domestic use of goods and services | 1.9 | 0.7 | -1.4 | 2.5 | -0.5 |
| Final consumption expenditure of households and NPISH | 2.0 | 0.1 | 0.9 | 1.0 | 0.5 |
| Final consumption expenditure of general government | 2.7 | 0.5 | 0.8 | 0.1 | 0.5 |
| Gross fixed capital formation (GFCF) | 0.6 | 0.6 | -3.5 | -0.6 | -1.3 |
| Total exports | 2.7 | 3.3 | 3.4 | -3.4 | -0.1 |
| Total imports | 1.9 | 5.4 | -2.6 | 2.7 | -1.3 |
| Employed persons | 1.1 | 0.3 | 0.2 | 0.1 | 0.2 |
| Total hours worked | 1.6 | 0.3 | 0.2 | -0.1 | 0.2 |
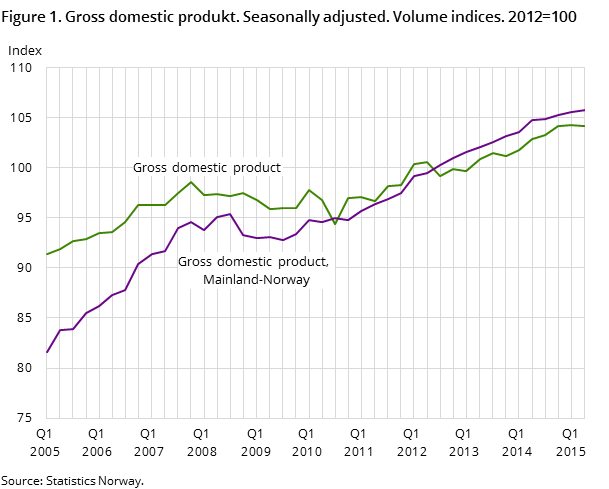
Value added in manufacturing and mining fell in the 2nd quarter by 1.5 per cent. This is the second quarter in a row with a marked decline. The decline in manufacturing and mining contributed to pulling down the growth in Mainland GDP by 0.2 percentage points. This decline is largely linked to reduced production within oil and gas-related industries. The fall in manufacturing is somewhat softened by growth in resource-based manufacturing products, like basic chemicals and basic metals.
Other goods-producing industries saw clear growth in the 2nd quarter. Production growth in construction, however, increased by only 0.1 per cent after a weak trend in the previous two quarters, while electricity production and fishing and aquaculture grew significantly in the 2nd quarter.
Value added in service industries excluding general government increased by 0.1 per cent from the 1st quarter to the 2nd quarter, after a moderate growth in the previous quarter. Also in the service industries, suppliers to the petroleum industry contributed to pulling down the growth. Value added in the general government increased by 0.4 per cent in Q2.
Value added in petroleum activities and ocean transport declined 1 per cent in the 2nd quarter, which contributed to a slight decline in total GDP compared with the previous quarter.
Good growth in consumption
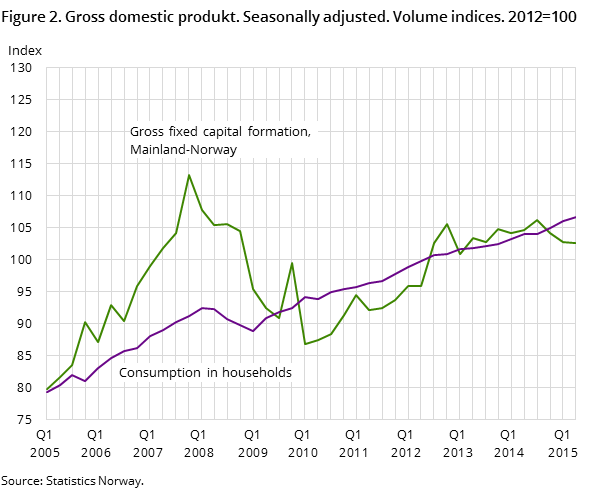
Household consumption rose by 0.6 per cent in the 2nd quarter, after two quarters in a row with significant growth. Consumption of goods increased 1.1 per cent. In particular, purchases of vehicles and electricity contributed to the rise. Consumption of services rose 0.6 per cent in the 2nd quarter.
Household consumption abroad grew by 0.3 per cent in the 2nd quarter. This weak development must be seen in conjunction with the strong increase last quarter.
Consumption in general government was 0.5 per cent up in the 2nd quarter, after a weak growth in the 1st quarter.
Decreased investments
Gross fixed capital formation (GFCF) in Mainland Norway declined by 0.3 per cent in the 2nd quarter, following a decline in the two preceding quarters. GFCF in manufacturing and mining fell by 1.3 per cent, following a decline of approximately 20 per cent in the 1st quarter.
Government GFCF dropped slightly in the 2nd quarter, but GFCF in the first half of 2015 remained 2.6 per cent higher than in the second half of 2014. Investments in dwellings grew by 1.4 per cent, after growth in the previous quarter, following a weak 2014.
The preliminary figures show that GFCF in the petroleum industry fell 3 per cent in the 2nd quarter. Investments peaked in the 3rd quarter of 2013, and then decreased gradually, with a temporary slight increase in the preceding quarter.
Increased exports of traditional goods excluding refined petroleum products
Exports of traditional goods fell by 0.2 percent in the 2nd quarter. Traditional goods also include some refined oil products, which have generally decreased. Looking at exports of traditional goods excluding refined oil products, this shows an increase of 3.2 per cent from the 1st to 2nd quarter.
Imports of traditional goods were approximately unchanged from the 1st to 2nd quarter, after a growth of 2.5 per cent in the previous quarter. Total imports of goods and services decreased by 1.3 per cent.
Employment growth
From the 1st to 2nd quarter, employment increased by 0.2 per cent, which corresponds to around 5 500 people, while the increase in the 1st quarter was approximately 3 000.
Number of hours worked increased by 0.2 per cent in the 2nd quarter, similar to employment, after a 0.1 per cent decrease in the previous quarter.
1st quarter of 2015 is revised
In connection with the release of figures for the 2nd quarter, new information has been incorporated into the figures for the 1st quarter of 2015. Volume growth in GDP for Mainland Norway from the 1st quarter of 2014 to the 1st quarter of 2015 remains unchanged from the previous release despite the revision of individual components . The seasonally-adjusted GDP growth for Mainland Norway, however, is now somewhat weaker in the 1st quarter than in the previous release. This is because the seasonally-adjusted figures for previous quarters are affected when figures for a new quarter are available.
For an overview of the revisions in the main aggregates in the last quarters, see table 48.
For more information on compilation methods and seasonal adjustment practice, please see About the statistics and On seasonal adjustment of the quarterly national accounts.
For an overview of the development in the GDP of some of our trading partners, please refer to the link to OECD statistics under Other websites.
Main revision of the national accountsOpen and readClose
Statistics Norway has made a main revision to the national accounts. The first results from this revision were published on 20 November 2014. The revisions are partly due to new international recommendations on national accounting and partly the results of improved methods of estimations and new sources. Read more about the main revision.
Concepts and definitions in National AccountsOpen and readClose
For more information about definitions of the main concepts, variables and classifications in national accounts, see About the statistics, definitions.
How the figures are calculatedOpen and readClose
The sum of four quarters in the Quarterly National Accounts (QNA) makes up the preliminary annual figures until the Annual National Accounts (ANA) for year t are published in November in year t+2 and incorporated as a new base year in the QNA. Hence, 2011 is the base year in the QNA when publishing data in May 2014.
In both the ANA and QNA, the figures stripped of movements in prices are referred to as volume changes, or fixed price estimates in the QNA, and this is done to identify the underlying cyclical pattern of the economy.
Note that in the time series in volume, the figures from the base year and onwards are fixed price figures, while data prior to the base year are chained volume figures. This implies that additivity in volume is lost prior to the base year.
Contact
-
Pål Sletten
E-mail: pal.sletten@ssb.no
tel.: (+47) 99 29 06 84
-
Ingunn Sagelvmo
E-mail: ingunn.sagelvmo@ssb.no
tel.: (+47) 40 90 26 32
-
Pia Tønjum
E-mail: pia.tonjum@ssb.no
tel.: (+47) 48 99 12 07
-
Kristian Gimming
E-mail: kristian.gimming@ssb.no
tel.: (+47) 91 88 39 06
